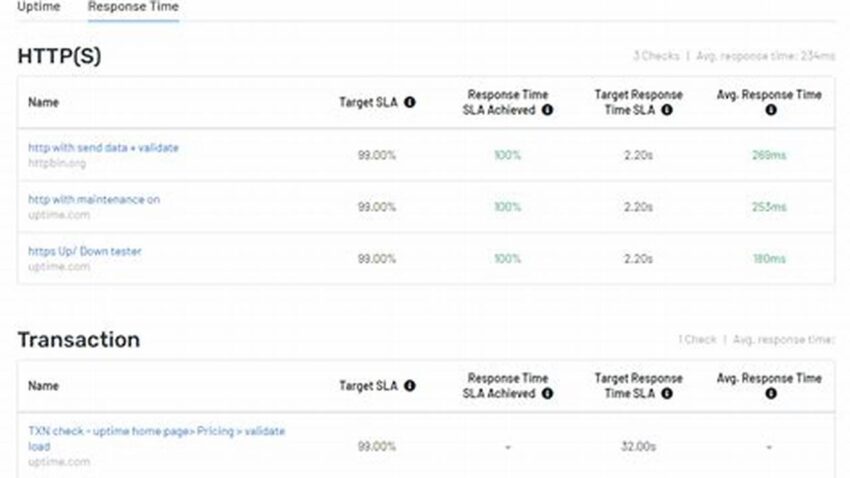
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) are contractual agreements that define the expected performance of a service. A critical component within an SLA is the uptime guarantee, which specifies the percentage of time a service is expected to be operational and accessible. Comprehending these guarantees is crucial for businesses relying on services to support their operations, ensuring predictable performance and mitigating potential disruptions.
Importance of Availability
High availability minimizes revenue loss due to service interruptions and maintains customer satisfaction.
Financial Implications
SLAs often include penalties for providers failing to meet the guaranteed uptime, offering financial recourse for service disruptions.
Performance Metrics
Clearly defined metrics ensure objective measurement and transparent reporting of service availability.
Data Integrity and Security
Uptime guarantees contribute to maintaining data integrity and security by minimizing potential downtime risks.
Business Continuity
Reliable service availability ensures business operations can continue uninterrupted, minimizing downtime impact.
Disaster Recovery
SLAs often outline disaster recovery procedures, ensuring a swift return to service in case of unforeseen events.
Maintenance and Upgrades
Scheduled maintenance windows are typically defined within SLAs to minimize disruptions and ensure planned downtime is communicated.
Negotiation and Agreement
Understanding the components of an uptime guarantee allows for informed negotiation and agreement on realistic and achievable service levels.
Monitoring and Reporting
Effective monitoring and reporting mechanisms are essential for tracking service availability and ensuring compliance with agreed-upon metrics.
Vendor Accountability
SLAs hold service providers accountable for delivering the promised uptime, promoting transparency and reliability.
Tips for Evaluating Uptime Guarantees
Realistic Expectations: Consider industry standards and the specific service’s nature when evaluating the feasibility of an uptime guarantee.
Clearly Defined Metrics: Ensure the metrics used to measure uptime are unambiguous and easily verifiable.
Exclusions and Limitations: Understand any exclusions or limitations to the uptime guarantee, such as scheduled maintenance or force majeure events.
Remediation and Compensation: Clarify the procedures for remediation and compensation in case of SLA breaches.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between 99.9% and 99.99% uptime?
While seemingly small, the difference translates to significantly more potential downtime. 99.9% allows for over 8 hours of downtime per year, while 99.99% allows for less than an hour.
What are typical uptime guarantees for different service types?
Uptime guarantees vary depending on the service. Critical services like web hosting often aim for 99.99% or higher, while less critical services may have lower guarantees.
What happens if a provider fails to meet the agreed-upon uptime?
Typically, the SLA will outline penalties or service credits for breaches of the uptime guarantee. The specific consequences should be clearly defined in the agreement.
How is uptime typically measured?
Uptime is usually measured by monitoring systems that track the availability of the service from multiple locations. These systems often use pings or other network requests to verify availability.
What are some common exclusions to uptime guarantees?
Common exclusions include scheduled maintenance, emergency maintenance due to unforeseen circumstances, and issues outside the provider’s control, such as network outages beyond their network.
How can I ensure my provider adheres to the SLA?
Regularly review the provider’s performance reports and independently monitor the service’s availability. Open communication with the provider is essential for addressing any concerns or discrepancies.
A thorough understanding of uptime SLAs empowers businesses to make informed decisions about service providers, negotiate favorable terms, and ensure the reliability and availability of critical services. This proactive approach minimizes potential disruptions, safeguards business operations, and fosters a strong foundation for growth and success.