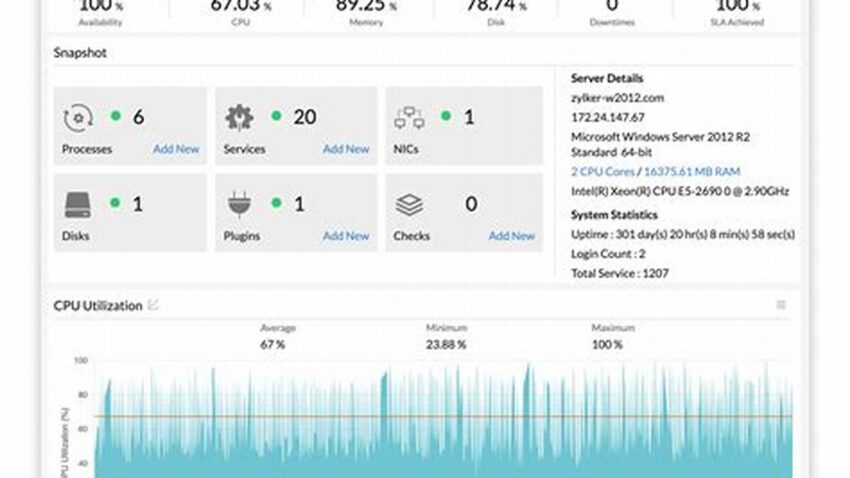
Maintaining operational continuity is paramount for any online service. For Linux-based servers, this translates to ensuring consistent availability and performance. Proactive vigilance regarding server status is crucial for preventing disruptions and maintaining service reliability. This involves implementing robust processes for tracking server availability and rapidly addressing any downtime.
Real-Time Status Awareness
Continuous monitoring provides immediate notification of server failures, enabling swift corrective action.
Performance Bottleneck Identification
Monitoring tools help pinpoint performance issues, allowing administrators to optimize server resources and prevent slowdowns.
Data Loss Prevention
Early detection of potential problems can prevent data loss due to hardware failures or other critical incidents.
Enhanced Security Posture
Monitoring can reveal unusual activity that might indicate security breaches, allowing for timely intervention.
Improved Resource Allocation
Analyzing uptime data informs resource allocation decisions, ensuring optimal server performance and cost efficiency.
Reduced Downtime Costs
Minimizing downtime translates directly to reduced financial losses due to service interruptions.
Proactive Maintenance
Monitoring data can predict potential failures, enabling proactive maintenance and preventing unexpected outages.
Service Level Agreement Compliance
Consistent uptime is essential for meeting service level agreements (SLAs) and maintaining customer satisfaction.
Trend Analysis and Forecasting
Historical uptime data facilitates trend analysis, enabling administrators to forecast future needs and proactively scale resources.
Improved Customer Experience
Reliable server operation ensures a seamless and positive experience for end-users, fostering trust and loyalty.
Tips for Effective Implementation
Select the Right Tools
Choose monitoring tools that align with specific needs and provide comprehensive metrics.
Establish Clear Alerting Thresholds
Define appropriate thresholds for alerts to avoid notification fatigue and ensure timely responses to critical issues.
Regularly Review Monitoring Data
Consistent review of monitoring data helps identify recurring problems and optimize server performance over time.
Develop a Response Plan
Establish a clear plan of action for responding to downtime alerts to minimize service disruptions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key metrics to monitor for Linux server uptime?
Essential metrics include CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, network traffic, and service availability.
How frequently should server uptime be monitored?
The ideal monitoring frequency depends on the specific application and its criticality. Real-time monitoring is often recommended for mission-critical systems.
What are some popular tools for Linux server uptime monitoring?
Commonly used tools include Nagios, Zabbix, Prometheus, and Grafana.
How can monitoring be integrated with existing infrastructure?
Many monitoring tools offer integration with various platforms and services, allowing for seamless incorporation into existing workflows.
What are the best practices for configuring uptime alerts?
Best practices include setting clear notification thresholds, defining escalation procedures, and regularly testing alert functionality.
What is the difference between uptime and availability?
Uptime refers to the continuous duration a server has been operational. Availability refers to the percentage of time a server is accessible and functioning as intended, often accounting for planned maintenance.
By implementing robust monitoring practices, organizations can ensure the continuous availability, performance, and security of their Linux servers, contributing significantly to overall operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.