System administrators often require information about a system’s operational history, particularly the duration it has been running since its last restart. This duration, known as uptime, is a crucial metric for performance monitoring, troubleshooting, and maintenance scheduling. Accessing this information requires specific commands tailored to the operating system. This article focuses on methods for retrieving uptime in both Windows and Linux environments, providing a concise guide for system administrators.
Importance of Checking Uptime
Uptime monitoring helps identify instability issues, track the effectiveness of system updates, and schedule necessary downtime for maintenance.
Understanding Windows Uptime Retrieval
Windows offers several methods to check uptime, including using the Task Manager, the systeminfo command, and PowerShell cmdlets.
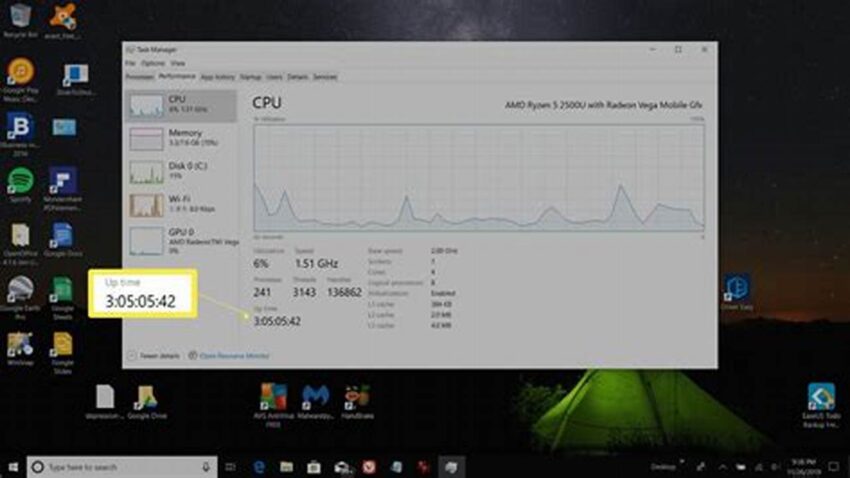
Using the Task Manager
The Task Manager’s Performance tab provides a basic uptime display.
Leveraging the systeminfo Command
The `systeminfo` command offers a more detailed report, including the system boot time.
Employing PowerShell for Uptime Checks
PowerShell provides cmdlets that allow for scripting and automated uptime monitoring.
Accessing Uptime in Linux
The `uptime` command in Linux provides a concise summary of the system’s uptime, load average, and currently logged-in users.
Interpreting the Linux uptime Command Output
Understanding the output of the `uptime` command provides valuable insights into system performance.
Practical Applications of Uptime Information
Uptime data is essential for various tasks, including performance analysis, troubleshooting, and capacity planning.
Tips for Effective Uptime Monitoring
Regularly checking uptime helps identify potential problems early on.
Integrating Uptime Checks into Monitoring Systems
Incorporate uptime checks into automated monitoring tools for proactive alerts and reports.
Using Uptime Data for Performance Analysis
Correlate uptime with performance metrics to identify trends and potential bottlenecks.
Documenting Uptime and Downtime
Maintain a log of uptime and downtime for historical analysis and reporting.
How can I check the uptime of a remote Windows server?
PowerShell remoting or dedicated monitoring tools can retrieve uptime from remote Windows servers.
What are the common reasons for frequent reboots in Linux?
Kernel updates, hardware issues, or application crashes can lead to frequent reboots.
How can uptime information be used for capacity planning?
Long uptimes can indicate system stability and inform decisions about resource allocation.
Is there a way to automate uptime checks in Linux?
Cron jobs and system monitoring tools can automate uptime checks and generate alerts.
How can I access historical uptime data?
System logs and dedicated monitoring tools typically store historical uptime data.
What are the limitations of relying solely on uptime as a performance indicator?
While uptime is valuable, it doesn’t provide a complete picture of system health and should be considered alongside other metrics.
Understanding and monitoring system uptime is fundamental for effective system administration. By utilizing the tools and techniques described, administrators can gain valuable insights into system stability, performance, and resource utilization, ultimately contributing to a more reliable and efficient IT infrastructure.