Determining system uptime is a fundamental task for Windows administrators and users alike. It provides crucial information for troubleshooting, performance analysis, and system maintenance. Knowing how long a system has been running can help pinpoint the source of recent issues, assess stability, and schedule necessary updates or restarts.
1. Importance of System Uptime Monitoring
Tracking uptime allows administrators to identify instability patterns and potential hardware or software problems.
2. Using the `systeminfo` Command
The `systeminfo` command provides comprehensive system information, including boot time, which can be used to calculate uptime.
3. Utilizing the `net statistics` Command
The `net statistics` command offers a quicker way to view system uptime since the last restart.
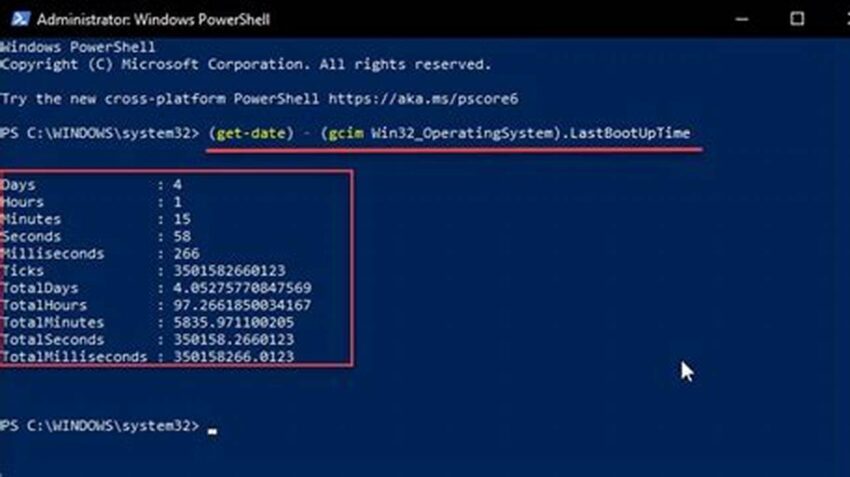
4. Leveraging PowerShell’s `Get-WmiObject` Cmdlet
PowerShell’s `Get-WmiObject` cmdlet allows access to detailed system information, including last boot time, for precise uptime calculations.
5. Task Manager for Quick Uptime Checks
The Task Manager’s Performance tab provides a readily accessible view of system uptime.
6. Uptime as an Indicator of System Stability
Consistently short uptimes can indicate underlying system issues requiring investigation.
7. Uptime and Security Patching
Long uptimes might suggest a system is overdue for security patches and updates.
8. Uptime in Performance Troubleshooting
Correlating uptime with performance issues can help identify resource leaks or other performance bottlenecks.
9. Uptime and Scheduled Maintenance
Knowing system uptime is essential for scheduling downtime for maintenance tasks without disrupting operations.
10. Automated Uptime Monitoring Tools
Various tools and scripts can automate uptime monitoring and provide alerts based on predefined thresholds.
Tip 1: Using Command Prompt Shortcuts
Create shortcuts for frequently used uptime commands for quick access.
Tip 2: PowerShell Scripts for Advanced Uptime Tracking
Develop PowerShell scripts to automate uptime data collection and reporting.
Tip 3: Integrating Uptime Monitoring with System Monitoring Tools
Integrate uptime monitoring into broader system monitoring tools for a comprehensive system health overview.
Tip 4: Interpreting Uptime Data in Context
Always analyze uptime data in conjunction with other system metrics for a more accurate diagnosis of potential issues.
How can I quickly check system uptime from the command line?
The `net statistics` command offers the fastest way to view uptime from the command prompt.
What if the `systeminfo` command takes too long to execute?
Consider using the `net statistics` or Task Manager for a quicker view of uptime. For more detailed information, leverage PowerShell’s `Get-WmiObject` cmdlet.
Why is tracking system uptime important?
Tracking uptime is crucial for troubleshooting, performance analysis, security management, and maintenance planning.
Are there any automated solutions for uptime monitoring?
Yes, various tools and scripts are available to automate uptime monitoring and alerting.
How can I use PowerShell to get uptime information?
Use the `Get-WmiObject` cmdlet in PowerShell to access detailed system information, including last boot time, which allows for precise uptime calculation.
What does unusually short uptime indicate?
Frequent system restarts and short uptimes can indicate underlying hardware or software problems.
Understanding and monitoring Windows system uptime is a vital aspect of system administration and maintenance. By utilizing the available command-line tools and techniques outlined above, users can gain valuable insights into their system’s stability, performance, and overall health.