Determining system uptime is a fundamental task for system administrators and users alike. It provides valuable insights into system stability, performance, and potential issues. Knowing how long a Windows system has been running can be crucial for troubleshooting, scheduling maintenance, and assessing the impact of software updates or hardware changes. Accessing this information through the command line offers a quick and efficient method, especially useful in remote administration or scripted scenarios.
Quick Access to System Information
The command-line approach offers immediate access to uptime data without navigating graphical interfaces.
Remote Administration Capabilities
Checking uptime remotely becomes streamlined through command-line tools, facilitating system management across networks.
Automation Potential
Integrating uptime checks into scripts allows for automated monitoring and reporting, enhancing system management efficiency.
Troubleshooting Aid
Uptime duration can be a valuable clue when diagnosing system instability or performance problems.
Performance Analysis
Tracking uptime helps identify patterns and correlations between system uptime and performance metrics.
Maintenance Scheduling
Uptime information informs decisions about optimal times for system reboots and maintenance activities.
Security Auditing
Unexpectedly short uptime durations can indicate potential security breaches or unauthorized system restarts.
Resource Monitoring
Long uptimes can sometimes lead to resource depletion; monitoring uptime helps preemptively address such situations.
Tips for Utilizing Command-Line Uptime Checks
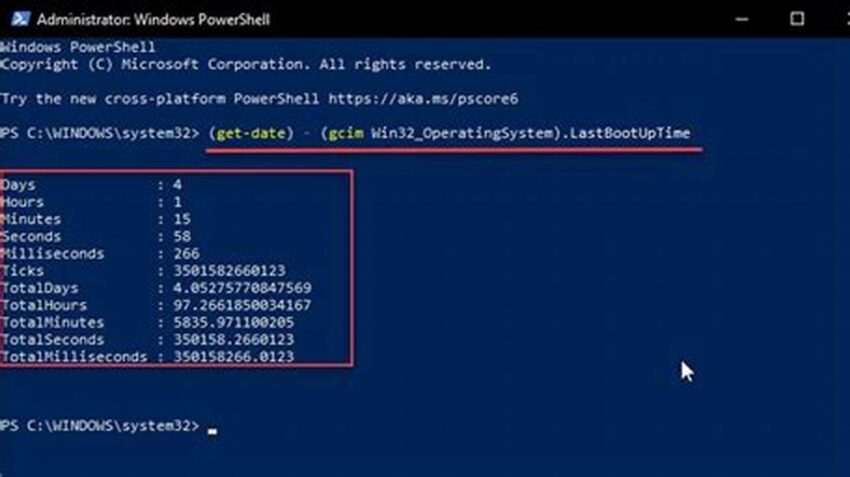
Tip 1: Using PowerShell: The `Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object LastBootUpTime` command provides comprehensive uptime information in PowerShell.
Tip 2: Employing systeminfo: The `systeminfo` command offers a broader system overview, including uptime, within the command prompt.
Tip 3: Scripting for Automation: Integrate uptime commands into batch scripts or PowerShell scripts for automated reporting and monitoring.
Tip 4: Remote Execution: Utilize tools like PowerShell Remoting or PsExec to execute uptime commands on remote Windows systems.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I check Windows uptime using the command prompt?
The `systeminfo` command provides uptime information, among other system details.
What is the PowerShell equivalent for checking uptime?
`Get-CimInstance Win32_OperatingSystem | Select-Object LastBootUpTime` retrieves uptime data in PowerShell.
Can I automate uptime checks?
Yes, integrating uptime commands into scripts enables automated monitoring and reporting.
How can I check uptime on a remote Windows machine?
Tools like PowerShell Remoting and PsExec facilitate remote execution of uptime commands.
Why is knowing system uptime important?
Uptime information is crucial for troubleshooting, maintenance scheduling, performance analysis, and security auditing.
What does a short uptime indicate?
A shorter-than-expected uptime can signal recent restarts due to updates, crashes, or potential security issues.
Mastering the command-line approach to checking Windows uptime empowers users with a versatile and efficient tool for system administration and maintenance. Its adaptability for scripting and remote execution makes it an invaluable asset for both individual users and large-scale IT environments.