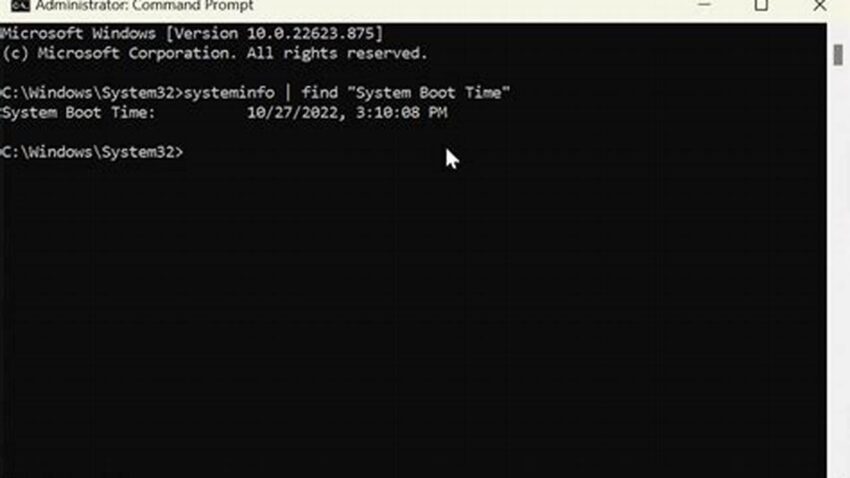
Determining the duration a computer system has been running since its last restart, often referred to as system uptime, provides valuable insights into system stability, performance, and potential issues. Accessing this information through the command prompt offers a quick and efficient method, especially useful for system administrators and troubleshooters.
Importance of System Uptime
Extended uptime can indicate a stable and well-maintained system. Conversely, frequent restarts might signal underlying hardware or software problems requiring investigation.
Performance Analysis
Correlating uptime with performance metrics can reveal performance degradation over prolonged operation, suggesting necessary maintenance or resource optimization.
Troubleshooting
Uptime information assists in troubleshooting by providing context for error occurrences and identifying potential triggers related to system duration.
Security Auditing
Tracking uptime contributes to security auditing by helping pinpoint unauthorized restarts or system compromises.
Scheduled Maintenance
Knowing system uptime assists in planning scheduled maintenance and minimizing disruptions.
Resource Monitoring
Uptime data complements resource monitoring, allowing administrators to observe resource usage patterns over extended periods.
Software Update Management
Uptime information helps determine optimal times for software updates and reboots to minimize user impact.
Hardware Reliability Assessment
Long uptimes can indicate reliable hardware performance, while frequent unexpected restarts might suggest hardware issues.
Incident Response
Uptime data plays a role in incident response by providing a timeline of system activity before and after an incident.
System Health Monitoring
Monitoring system uptime contributes to overall system health assessments and proactive maintenance planning.
Tips for Utilizing System Uptime Information
Regularly check uptime to establish a baseline for normal operation and identify deviations.
Compare uptime data with performance logs to pinpoint performance bottlenecks related to extended operation.
Include uptime information in troubleshooting documentation to provide valuable context for problem analysis.
Use uptime tracking to ensure adherence to scheduled maintenance windows and minimize downtime.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is uptime affected by sleep mode?
Sleep mode generally does not interrupt uptime, as the system remains technically running, albeit in a low-power state.
Does uptime reset after a power outage?
Yes, an unexpected power outage forces a system shutdown, resetting the uptime counter upon restart.
Can uptime be manipulated?
While technically possible to alter uptime records, doing so is generally discouraged as it undermines the data’s integrity for troubleshooting and analysis.
How does uptime differ from system boot time?
System boot time refers to the specific time and date of the last system start, while uptime represents the duration the system has been running since that boot time.
Where is uptime information stored?
Uptime information is typically maintained within the operating system kernel and accessed through system commands or utilities.
Are there tools beyond the command prompt for checking uptime?
Yes, various system monitoring tools and utilities provide uptime information alongside other system metrics.
Understanding and utilizing system uptime information effectively contributes to maintaining a stable, reliable, and well-performing computing environment. Leveraging the readily available command-prompt method provides a simple yet powerful tool for administrators and users alike.