Understanding how long a computer system has been running continuously, often referred to as uptime, can be valuable for troubleshooting, performance analysis, and system maintenance. This information provides insights into potential instability, the effectiveness of recent updates, and the overall health of the machine. Access to straightforward instructions for checking uptime on both Windows and macOS platforms empowers users to monitor their systems effectively.
1. System Stability Indicator
Extended uptime can sometimes indicate a stable system, free from recent crashes or forced restarts.
2. Troubleshooting Aid
Knowing the uptime helps pinpoint the timing of potential issues, correlating them with software installations or system changes.
3. Performance Analysis
Long uptimes can reveal performance degradation over time, prompting investigations into resource usage or accumulating background processes.
4. Update Effectiveness Assessment
Checking uptime after updates helps verify whether the system has remained stable following the changes.
5. Security Monitoring
Unexpected reboots might suggest unauthorized access or malware activity, making uptime a relevant security metric.
6. Scheduled Maintenance
Tracking uptime allows for better planning of necessary restarts for maintenance tasks and software installations.
7. Server Monitoring
For servers, uptime is a critical metric, reflecting service availability and reliability.
8. Resource Utilization
Prolonged uptime can lead to increased resource consumption by some applications; monitoring uptime helps identify potential resource leaks.
9. System Health Check
Uptime information contributes to a comprehensive system health assessment, alongside other performance indicators.
10. Post-Incident Analysis
After a system crash or failure, uptime data assists in determining the duration of the disruption and its potential impact.
Tip 1: Regular Checks
Incorporate uptime checks into regular system maintenance routines for proactive monitoring.
Tip 2: Log Analysis
Combine uptime data with system logs for a more complete picture of system events and potential issues.
Tip 3: Utilize Monitoring Tools
Explore system monitoring tools that automatically track uptime and other key metrics.
Tip 4: Document Uptime
Maintain a record of uptime data to track trends and identify recurring problems.
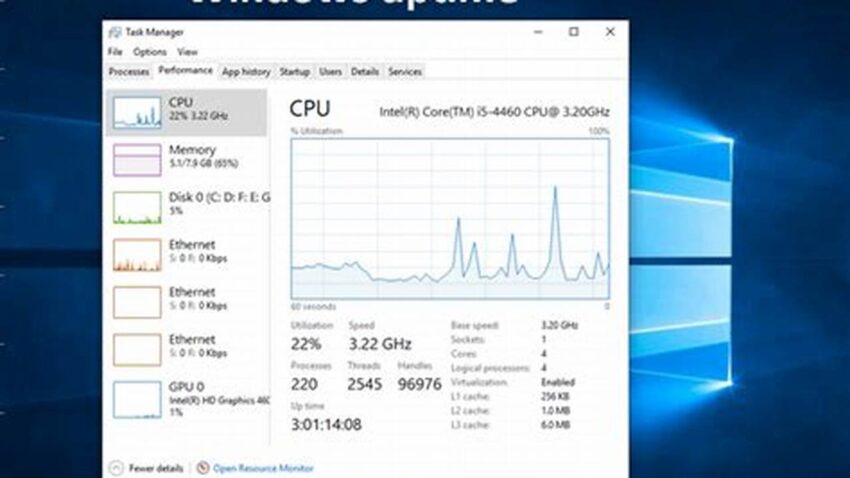
How can I check uptime on Windows?
The Task Manager, System Information tool, or the command prompt (using the `systeminfo` command) provide uptime information on Windows systems.
What is the command to check uptime on macOS?
The `uptime` command in the Terminal application displays macOS system uptime.
Why is my uptime unexpectedly short?
Unexpectedly short uptime might indicate recent crashes, forced restarts due to updates, or power outages.
Is longer uptime always better?
While long uptime can suggest stability, it’s not the sole indicator of system health. Regular restarts are often necessary for applying updates and clearing temporary files.
How does uptime relate to system performance?
While not directly correlated, prolonged uptime can sometimes lead to decreased performance due to accumulating temporary files or resource leaks.
Where can I find more detailed guides for checking uptime?
Online tutorials and platform-specific documentation provide comprehensive instructions for checking uptime on various operating systems.
Monitoring system uptime is a simple yet valuable practice for maintaining optimal computer performance and stability. Utilizing readily available tools and techniques empowers users to proactively identify potential issues and ensure the smooth operation of their systems.