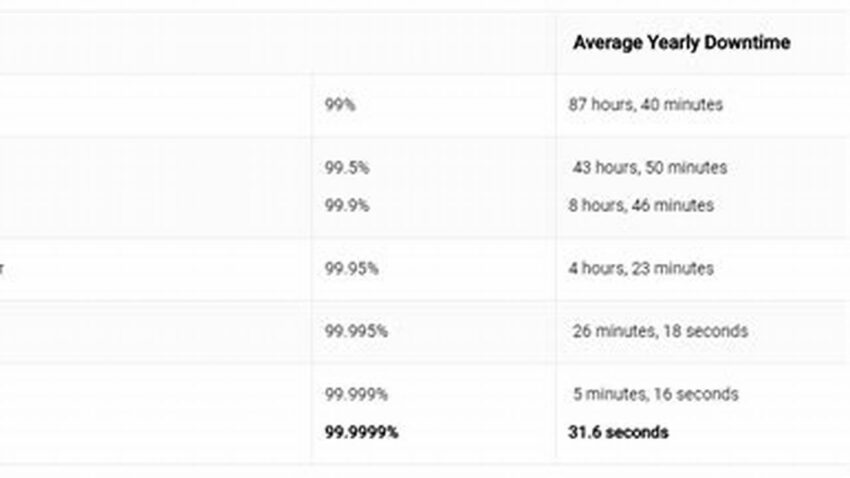
High availability is a critical aspect of modern server infrastructure. A system boasting 99.99% uptime, often referred to as “four nines,” experiences minimal downtime, ensuring consistent service delivery and minimizing potential revenue loss or user disruption. This level of reliability requires meticulous planning, robust system design, and proactive maintenance. A Linux-based approach offers a powerful and flexible platform for achieving this goal, leveraging its open-source nature, extensive community support, and granular control over system resources.
Redundancy
Implementing redundant hardware components, such as power supplies, network interfaces, and storage devices, safeguards against single points of failure.
Monitoring
Comprehensive monitoring tools provide real-time insights into system performance, allowing for proactive identification and resolution of potential issues.
Failover Mechanisms
Automated failover systems ensure seamless transition to backup resources in case of primary component failure.
Load Balancing
Distributing traffic across multiple servers prevents overload on individual machines, enhancing performance and resilience.
Security Hardening
Regular security updates and robust firewall configurations protect against vulnerabilities that could lead to downtime.
Disaster Recovery Planning
A well-defined disaster recovery plan outlines procedures for restoring services in the event of catastrophic failures.
System Updates
Regularly applying system updates and patches addresses known vulnerabilities and improves system stability.
Performance Tuning
Optimizing system parameters and configurations enhances performance and reduces the risk of resource exhaustion.
Testing and Validation
Thorough testing and validation procedures ensure the effectiveness of implemented redundancy and failover mechanisms.
Documentation
Comprehensive documentation facilitates troubleshooting and maintenance, reducing downtime during issue resolution.
Tips for Achieving High Availability
Regular Audits
Conduct periodic system audits to identify potential weaknesses and ensure compliance with best practices.
Automated Maintenance
Automate routine maintenance tasks, such as backups and security updates, to minimize manual intervention and human error.
Capacity Planning
Proactively assess resource utilization and plan for future growth to prevent performance bottlenecks.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing
Foster collaboration among system administrators and encourage knowledge sharing to improve overall system management.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the business benefits of achieving high availability?
High availability minimizes service disruptions, leading to increased customer satisfaction, improved brand reputation, and reduced revenue loss.
How does Linux contribute to high availability?
Linux offers a stable and customizable platform with a vast ecosystem of tools and technologies designed for high availability deployments.
What are some common challenges in implementing high availability?
Challenges can include the complexity of configuration, the cost of redundant hardware, and the need for specialized expertise.
How can I measure the success of my high availability implementation?
Key metrics include mean time to recovery (MTTR), mean time between failures (MTBF), and overall system uptime.
What are the first steps in planning for high availability?
Begin by identifying critical systems and services, assessing potential risks, and defining acceptable downtime thresholds.
Is high availability achievable on a limited budget?
While high availability solutions can involve upfront costs, open-source tools and strategic planning can help minimize expenses.
Building a highly available system is an ongoing process requiring continuous monitoring, adaptation, and improvement. By adhering to best practices and leveraging the power of Linux, organizations can achieve the desired levels of uptime and ensure the consistent delivery of critical services.