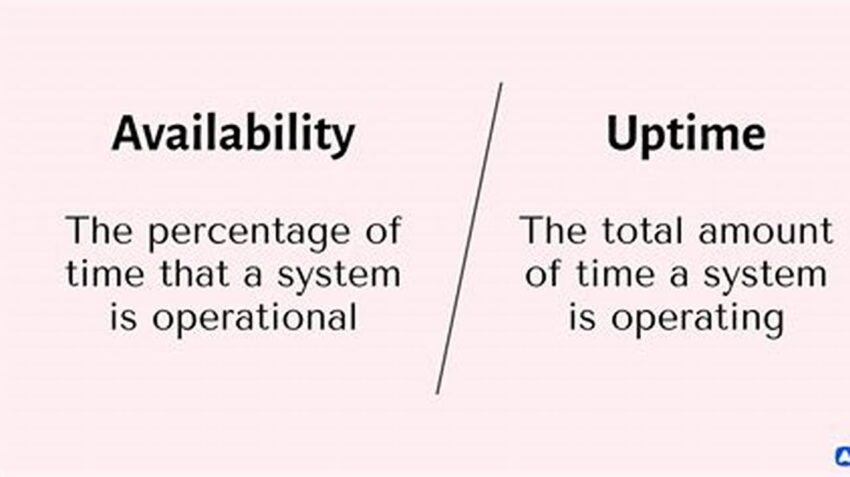
System availability is a critical aspect of any online service or infrastructure. This document explores the core concept of ensuring consistent operational status, providing a clear and concise overview of its significance and practical implications.
Importance of Consistent System Availability
Uninterrupted operation is essential for maintaining user trust, supporting business continuity, and maximizing revenue generation. Downtime can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and lost productivity.
Impact on Business Operations
Consistent access to systems and services directly impacts an organization’s ability to conduct business, serve customers, and manage internal processes efficiently.
Relationship with Service Level Agreements (SLAs)
Defined availability targets are often formalized in SLAs, which establish contractual obligations between service providers and clients regarding expected operational performance.
Factors Affecting Operational Consistency
Various factors, including hardware failures, software bugs, network outages, and human error, can contribute to disruptions in service availability.
Strategies for Maintaining High Availability
Implementing redundancy, robust monitoring systems, and effective disaster recovery plans are crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring continuous operation.
Measuring and Tracking Operational Status
Key metrics, such as mean time between failures (MTBF) and mean time to recovery (MTTR), provide valuable insights into system reliability and performance.
Best Practices for Optimizing System Performance
Proactive maintenance, regular updates, and thorough testing are essential for preventing issues and optimizing system stability.
The Role of Monitoring and Alerting Systems
Real-time monitoring and automated alerts enable swift responses to potential problems, minimizing the impact of incidents and preventing extended outages.
Tips for Ensuring Consistent System Performance
Regular Maintenance: Implement a schedule of routine maintenance tasks, including system updates, security patches, and hardware checks.
Redundancy: Utilize redundant systems and infrastructure components to minimize the impact of single points of failure.
Disaster Recovery Planning: Develop a comprehensive disaster recovery plan that outlines procedures for restoring services in the event of a major outage.
Thorough Testing: Regularly test systems and processes to identify potential vulnerabilities and ensure the effectiveness of recovery mechanisms.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the consequences of unplanned downtime?
Unplanned downtime can result in financial losses, damage to reputation, and disruption of business operations.
How can organizations minimize the risk of downtime?
Implementing redundancy, robust monitoring systems, and effective disaster recovery plans can significantly reduce the risk of downtime.
What is the significance of MTBF and MTTR?
MTBF and MTTR are important metrics for assessing system reliability and the efficiency of recovery processes.
Why is proactive maintenance important?
Proactive maintenance helps prevent potential issues, optimize system stability, and minimize the likelihood of unplanned downtime.
What are the key components of a disaster recovery plan?
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan should include procedures for data backup and restoration, system recovery, and communication protocols.
How can monitoring systems improve availability?
Real-time monitoring enables prompt detection and resolution of issues, minimizing the impact of incidents and preventing extended outages.
Achieving and maintaining consistent operational status is a continuous process that requires proactive planning, diligent execution, and ongoing evaluation. By prioritizing system reliability, organizations can mitigate risks, enhance performance, and ensure the seamless delivery of critical services.